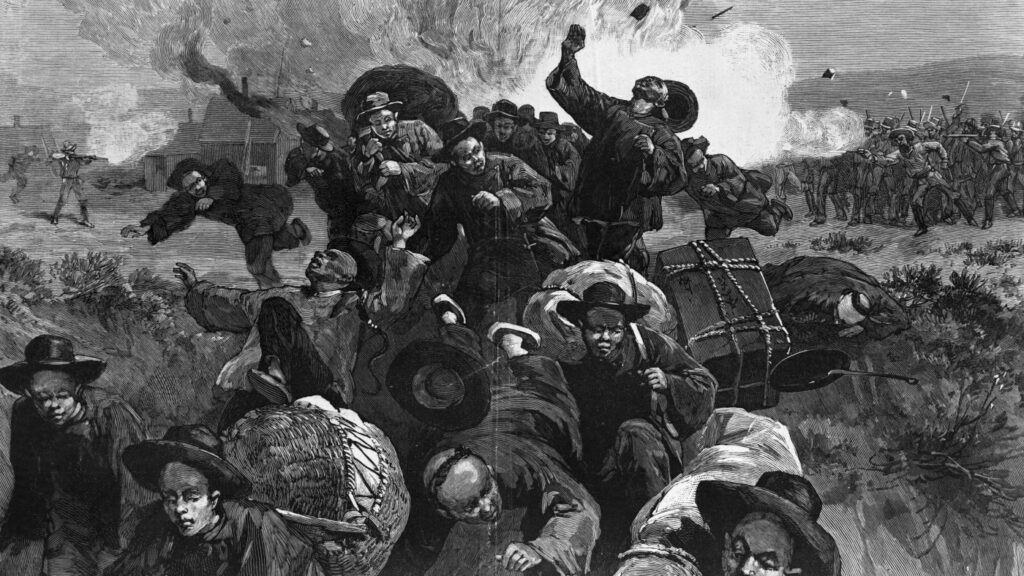
The Massacre of Chinese Americans at Rock Springs, Wyoming. Illustration by Thure de Thulstrup. Published in Harper’s Weekly, September 26, 1885.
Thure de Thulstrup/Getty Images
hide caption
toggle caption
Thure de Thulstrup/Getty Images
The Chinese Exclusion Act is widely considered to be the first significant crackdown on immigration in American history. It’s a riveting tale that parallels today and may provide insights into the economic consequences of immigration restrictions and mass deportations. This is Part 2 of that story, which explores the economic and political factors that led to the Act and examines what happened to the American economy after it was passed (Part 1 can be read here). Please note: this story includes racist quotes from the 19th century.
On May 10, 1869, the eyes of America focused on a makeshift ceremony in the middle of nowhere.
Two railroad companies had spent six years on one of the most ambitious infrastructure projects of the 19th century: the construction of the first transcontinental railroad. One company had built from the east. The other from the west. This was the day they finally met up and linked their tracks together.
The meeting point was a place called Promontory Summit in the desolate desert of northwest Utah. A thousand people — politicians, journalists, railroad executives and workers — traveled there for the monumental occasion.
As we covered in Part 1 of this story, this historic moment would not have been possible without the sacrifices of Chinese immigrants. They had played a crucial role in constructing the western part of the railroad — the most difficult and dangerous section to build. As many as 1,200 Chinese immigrants died constructing it. However, on this day of celebration, railroad executives decided to exclude their Chinese workers from the official ceremony and photographs. Ouch.
Railroad workers celebrate at the driving of the Golden Spike Ceremony in Utah on May 10, 1869 signifying completion of the first transcontinental railroad route created by joining the Central Pacific and Union Pacific Railroads.
Bettmann/Getty Images
hide caption
toggle caption
Bettmann/Getty Images
But Chinese Americans had reason to be hopeful in the wake of the transcontinental railroad’s completion. Since they began arriving in America a couple decades before, they had been the target of discriminatory laws and violence. But now national news reports praised them as skilled and productive workers making invaluable contributions to America’s economy.
“The Chinaman is a born railroad builder, and as such he is destined to be most useful to California, and, indeed, to the whole Pacific slope,” read one nationally circulated news report. The Daily Alta California, then the most popular newspaper in the state, declared that Chinese workers “do a better, neater, and cleaner job, and do it faster and cheaper than white laborers from the East.”
Political winds also seemed to be blowing in favor of Chinese Americans. In 1868, the United States signed the Burlingame Treaty, which strengthened diplomatic and trade relations with China and encouraged “free migration and emigration” between the two countries. In the decade to come, the Chinese population in America would swell by about 50 percent.
Even more, this was the post-Civil War Reconstruction era, when Radical Republicans were amending the U.S. Constitution and fighting for the civil rights of freed slaves. Many hoped that new constitutional amendments and civil rights laws would apply to other excluded groups — including Chinese immigrants. Back then, the only immigrants who were allowed to become American citizens and obtain equal rights were “free white persons.”
In 1870, U.S. Senator Charles Sumner (R-Massachusetts), one of America’s leading voices for abolition and civil rights, fought to open up a pathway for Chinese and other non-white immigrants to become citizens. But Western politicians, including in Sumner’s own more racially progressive Republican party, saw this proposal as politically radioactive.
In making his case against Sumner’s bill to open a pathway to citizenship for Chinese immigrants, Senator William Morris Stewart (R-Nevada) warned that the West Coast would be “overpowered by the mob element that seeks to exterminate the Chinese” if it passed, and that “they will be slaughtered before any one of them can be naturalized under your bill.”
The effort to expand citizenship and civil rights to Chinese immigrants failed to pass Congress. But the “mob element” — as Senator Stewart called it — would nonetheless make life miserable for Chinese Americans.
In an omen of the horrors to come, just one year later, a white mob in Los Angeles lynched 17 Chinese men and boys in a raid on Chinatown. It was one of the largest — if not the largest — mass lynching in American history. It became known as “the Chinese Massacre of 1871.”
All of this was before “The Panic of 1873,” a financial crisis that would plunge America’s economy into a long and miserable depression. In the depths of despair, white working-class Americans on the West Coast would rally around a new populist slogan: “The Chinese must go!”
The Long Depression And The Rise of Racist Populism
The completion of the transcontinental railroad may have, ironically, contributed to the coming populist backlash. For one, excitement over the transcontinental and other railroads led to a speculative bubble. Investors overestimated the money-making potential of railroads, and once the transcontinental railroad was up and running, reality began to set in about how much money railroads and related investments would actually make. When the bubble burst in 1873, it took the whole economy with it.
The transcontinental railroad also integrated what had been effectively two separate American economies into one. Like the adoption of container ships during the globalization era of the 20th and 21st centuries, the transcontinental railroad increased competition in the economy by making it easier and cheaper to distribute and sell products to faraway places. This bigger, more competitive market was great for consumers, economic efficiency, and the nation’s long-term economic growth. But, with the railroad now serving as a new pipeline for products, West Coast industries were suddenly forced to compete with the more efficient and mechanized industries of the East Coast. Nancy Qian, an economist at Northwestern University, says this made the economic downturn that followed the Panic of 1873 much worse in the West.
Even more, during and after completion of the railroad, Chinese immigrants became a more sought after workforce, which effectively put a target on their backs. Increasing numbers of white workers began to resent them. They saw them as a culturally alien workforce, willing and able to do all sorts of jobs for less pay. And it wasn’t just railroads. Chinese immigrants now worked in all sorts of West Coast industries, including manufacturing, agriculture, woodcutting, and mining. “While the Chinese constituted less than 10 percent of the population of California in 1870, they accounted for approximately 25 percent of the workforce,” writes Beth Lew-Williams in her book The Chinese Must Go: Violence, Exclusion, and the Making of the Alien in America.
As the economy cratered after the Panic of 1873, a scarcity of jobs led to a zero-sum mindset amongst white workers. Demagogues began to blame the labor competition posed by increasing numbers of Chinese immigrants for the miseries of white joblessness and meager pay. They painted Chinese immigrants as the servile tools of monopolistic corporations, which were becoming increasingly powerful in the rapidly industrializing United States. The mighty railroad companies — which now owned valuable land across the United States thanks to federal legislation that funded the transcontinental railroad — were a prominent example. Populists began to rail against big corporations for employing the cheap labor of Chinese immigrants instead of the labor of white people — many of whom, by the way, were also recent immigrants themselves.
In late 1877, an Irish immigrant in San Francisco named Denis Kearney founded The Workingmen’s Party of California. Kearney articulated a populist politics that combined pro-labor and anti-corporate rhetoric with virulent anti-Chinese racism.
In one famous demonstration, in October 1877, Kearney led a mob to Nob Hill, a fancy part of San Francisco where the West Coast railroad barons had built mansions. Kearney gave a fiery speech to 2,000 people in front of the home of Charles Crocker, an executive at Central Pacific Railroad who had been instrumental in recruiting Chinese workers to build the transcontinental railroad.
“The Central Pacific Railroad men are thieves, and will soon feel the power of the workingmen,” Kearney said. “When I have thoroughly organized my party, we will march through the city and compel the thieves to give up their plunder. I will lead you to the City Hall, clean out the police force, hang the Prosecuting Attorney, burn every book that has a particle of law in it, and then enact new laws for the workingmen. I will give the Central Pacific just three months to discharge their Chinamen.”
In another speech, in front of a crowd in Boston, Kearney said, “The capitalist thief and land pirate of California, instead of employing the poor white man of that beautiful and golden State, send across Asia, the oldest despotism on earth, and there contracting with a band of leprous Chinese pirates, brought them to California, and now uses them as a knife to cut the throats of honest laboring men in that State.”
In rabble-rousing speech after speech, it was Kearney who popularized the slogan, “The Chinese must go!”
Kearney and the Workingmen’s Party would fail to achieve lasting political power, but their ideas proved to be popular on the West Coast. By the late 1870s, the writing was on the wall for both national political parties: if they wanted to win elections in West Coast states, they would need to clamp down on Chinese immigration.
The Rise of Chinese Exclusion
Back in those days, Washington — which didn’t have much experience actually trying to regulate immigration — viewed immigration policy as something you cordially worked out with the origin countries of immigrants. American political elites also hoped to remain friendly with China, which they viewed as economically and geopolitically important. And so, in 1880, the administration of President Rutherford B. Hayes delicately worked with China to amend the Burlingame Treaty, which had encouraged the free flow of immigration between the two countries. This new treaty, the Angell Treaty, allowed the United States to “regulate, limit, or suspend” the flow of Chinese laborers to the country. Congress could now act.
In 1882, after a presidential election, they did just that. Congress passed a forceful bill halting immigration of Chinese workers for twenty years and requiring Chinese immigrants already in the United States to register with the government and obtain “passports” so they could prove their legal status (similar to a “green card” today).
However, President Chester A. Arthur — who had only recently been elevated to the presidency after James Garfield was assassinated — objected to the law and decided to veto it. He believed it was too harsh. In his veto message, Arthur said the law would damage diplomatic and trade relations with China, which he and many others believed were vital to American interests. He objected to provisions requiring Chinese Americans to register with the government and obtain documents to prove their legal status, calling it “undemocratic and hostile to the spirit of our institutions.”
Even more, Arthur said, America “profited” from the work of Chinese immigrants — a belief held by many of the West Coast’s business elites.
“They were largely instrumental in constructing the railways which connect the Atlantic with the Pacific,” President Arthur said. “The States of the Pacific Slope are full of evidences of their industry. Enterprises profitable alike to the capitalist and to the laborer of Caucasian origin would have lain dormant but for them.” Arthur contended that the Chinese immigrants could continue to help develop and enrich America and, basically, do jobs that white people didn’t want to do.
Arthur’s veto, however, proved to be a political disaster. Many Americans erupted with anger. The Knights of Labor, a growing national labor union, organized thousands of workers to protest it. Across California, townspeople burned and hanged President Arthur’s effigy. Members of Arthur’s own Republican party worried his veto meant that they would fail to win elections on the West Coast for the foreseeable future.
Facing a national outcry, Congress went back to the drawing board a few weeks later. And they passed a watered-down version of the bill, which President Arthur signed into law on May 6, 1882.
This 1882 law is now popularly known as “the Chinese Exclusion Act.” It banned both skilled and unskilled Chinese laborers from immigrating to the US for ten years. Symbolically and politically, this bill was a big deal: it was the first significant crackdown on immigration in American history, a message that the federal government opposed Chinese immigration, and a reaffirmation that Chinese immigrants already in America could never become citizens.
However, the Chinese Exclusion Act of 1882 was just one in a series of federal laws against Chinese immigrants — and, as Beth Lew-Williams makes clear in The Chinese Must Go, this 1882 law was actually quite ineffective. Basically, President Arthur and Congress threw a bone to the insurgent anti-Chinese movement, but they provided few resources for federal enforcement against Chinese immigration and introduced a bunch of loopholes that allowed Chinese immigrants to continue coming in.
In the years after the Act’s passage, West Coast newspapers and populist agitators grew angry that Chinese immigrants were still entering the country and demanded that the government do more. This was the beginning of what you might call the national fight against “illegal immigration” — because before this virtually all immigration to the United States was legal.
But the growing discontent with the first iteration of the Chinese Exclusion Act wasn’t just about its lack of enforcement and loopholes. For many white Americans, simply preventing the flow of new Chinese immigrants wasn’t enough. They wanted expulsions and deportations of the Chinese people who already lived here — even though the vast majority of them were here legally.
And soon white vigilantes would take matters into their own hands.
Vigilante Expulsion
By 1885, anti-Chinese forces in the West had become emboldened by the federal government’s actions declaring that Chinese immigration was, in fact, a problem that needed to be solved. But they were also frustrated that Chinese workers seemed to keep coming into the country. Even more, they were angry about the continued presence of Chinese people in their communities and workplaces.
The first purges of Chinese Americans in towns across the West began spontaneously in response to inciting incidents. But what began as a movement characterized by sporadic outbursts of violence would soon morph into a premeditated political strategy of ethnic cleansing.
In Eureka, California, on February 6, 1885, two Chinese men got into a dispute and began firing guns at each other. One of them accidentally shot a white city councilman crossing the street. Shortly after, a mob of white residents stormed into the city’s Chinatown chanting “Hang all the Chinamen!” and “Burn Chinatown!” City leaders, including the mayor, sheriff, and a Christian minister, intervened to prevent arson and murders, but white gangs looted Chinatown. And, within about 48 hours, local vigilantes rounded up Chinese residents — hundreds of people — forced them onto steamships bound for San Francisco and told them to never return again. It became known as “the Eureka method” of expulsion and was soon copied by neighboring cities.
Later that year, in Rock Springs, Wyoming, a fight broke out between some Chinese and white miners that quickly exploded into horrific violence. Both groups were employed by the Union Pacific Coal Company (the same Union Pacific that built half of the transcontinental railroad). White miners, themselves immigrants, had grown to resent Chinese miners. On numerous occasions, Union Pacific had brought in Chinese workers after white workers went on strike for better wages, leading the white miners to view their Chinese counterparts as low-wage scabs. (Union Pacific, however, had also brought in Scandinavian immigrants in a similar way, but that didn’t seem to elicit the same level of rage.) This particular fight was over whether Chinese or white workers would get to work in a particularly lucrative mine. It got very ugly very fast. After the dispute, a white mob descended on Chinatown, murdered 28 Chinese miners and wounded 15 others, drove the whole Chinese community out, and set their homes and stores ablaze. The incident was dubbed “The Rock Springs Massacre.”
In Tacoma, Washington, a couple months later, residents took a more methodical, premeditated approach. “The violence of Tacoma differed from incidents at Eureka and Rock Springs,” writes Lew-Williams. “The Tacoma expulsion was not a spontaneous act by a mob angered by a triggering incident. Rather, it was cold and deliberate collective action that was publicly announced well in advance.” Nonetheless, while it may have been more orderly and less sudden, it resembled “the Eureka method.” White vigilantes — including Mayor Jacob Weisbach and other local political leaders — forcibly expelled all of Tacoma’s Chinese residents, this time putting them on a train instead of boats. They then demolished Tacoma’s Chinatown.
“The Tacoma Method” of Chinese expulsion
Washington Historical Society
hide caption
toggle caption
Washington Historical Society
Truckee, California, took a different approach to Chinese expulsion. Truckee sits in the basin underneath the Sierra Nevada peaks where Chinese rail workers had painstakingly built tunnels to allow passage for the transcontinental railroad (see Part 1 of this story). It boomed in population during and after the railroad’s construction, and many Chinese rail workers made it their home. By 1870, around a third of Truckee’s population was of Chinese descent. It had one of the biggest Chinatowns in the United States.
White residents of Truckee had long made life difficult for its Chinese residents. In 1876, for instance, white militants — part of a secretive group called “The Caucasian League” — murdered a Chinese woodcutter and wounded others and then, despite a trial, were found innocent (these types of acquittals for racist thugs and vigilantes were common in the West back then). Over the years, Truckee’s Chinatown was burned in a series of mysterious — but actually not so mysterious — fires. In fact, after one such fire, the town forced their Chinese residents to build a new Chinatown across the Truckee River. This new Chinatown had no bridge, so they had to cross the river by ferry.
But this wasn’t enough for the white residents of Truckee. They wanted Chinese people gone from the area completely. In the winter of 1885-86, a local lawyer and newspaper owner named Charles McGlashan was inspired by the cascade of purges across the West Coast. However, by then, there seemed to be some growing political and legal blowback for these extralegal expulsions. The town of Eureka, for example, was being sued by their former Chinese denizens for reparations. National politicians condemned violence in places like Rock Springs.
It was within this context that McGlashan pioneered what became known as “The Truckee Method,” a relatively non-violent — but still violent — boycott and harassment campaign against Chinese businesses and white businesses that employed Chinese people. The aim was to starve the Chinese out by eliminating their local economic opportunities and making their lives miserable. The campaign proved successful in ridding the town of Chinese residents and was copied by numerous other towns up and down California. McGlashan became a leader in an anti-Chinese boycott movement across the state.
Over the course of 1885 and 1886, more than 160 communities across the West Coast would expel their Chinese inhabitants. And they made it abundantly clear to national politicians: many Western voters were not satisfied with the 1882 law.
In 1888, President Grover Cleveland — hoping to carry Western states in his upcoming reelection battle — signed into law another Chinese Exclusion Act that had more teeth than the first one. This one prohibited all Chinese laborers from coming into the country — whether or not they had resided in the United States previously. It was a policy that was easier to enforce and administer. It was also quickly implemented, leaving thousands of Chinese immigrants who had traveled abroad stranded and unable to return. It was also a policy that angered China and marked the beginning of an age in which the United States set restrictive immigration policy unilaterally.
After President Cleveland signed this legislation into law, many white westerners took to the streets to celebrate. This was only two years after the unveiling of the Statue of Liberty, which proclaimed that America was a refuge for “your tired, your poor, your huddled masses yearning to breathe free.”
Four years later, with the Geary Act, Washington renewed Chinese exclusion for another ten years, expanded the power of the federal government to enforce anti-Chinese immigration laws, and implemented the registration and “passport” system that President Arthur had called “undemocratic and hostile to the spirit of our institutions.”
The Chinese Exclusion Acts — and the mob violence, pogroms, boycotts, and other forms of expulsion — had their intended effect. In 1890, the US Census Bureau recorded 107,488 Chinese people living in the United States. In 1900, that number dropped to 89,863. And by 1910, it was 71,531. The restrictions on Chinese immigration would not begin to be lifted until World War II.
The Economic Effects of Chinese Exclusion
Historians have found that the economies of towns suffered after they kicked out their Chinese residents.
Eureka, California faced all sorts of economic problems. “For most white residents, the financial loss was immediate,” writes Jean Pfaelzer in her book Driven Out: The Forgotten War Against Chinese Americans. Businesses lost workers. “Some went into debt to pay higher salaries to new white employees.” Landlords lost tenants. Stores lost customers. Chinese entrepreneurs had run the laundries in the town, and now people were stuck with dirty clothes. Chinese vegetable growers had provided the town with its produce and their disappearance meant no more fresh veggies. “White residents tried their hands at growing their own vegetables but complained about their poor results, the lack of variety of food, and the rotting produce that was shipped north from San Francisco,” writes Pfaelzer.
It was similar in Truckee. “The Chinese were renters, shoppers, and low-paid laborers, and white agents made money from their legal, real estate, and commercial transactions,” writes Pfaelzer. Charles McGlashan, the leader of the anti-Chinese boycott, sought to replace Chinese laundromats with an “expensive steam laundry,” but it was “simply too large and expensive for the needs of the small railroad town, and the Truckee Laundry Association was sued by its major investors.” Truckee businesses desperately recruited white workers with advertisements, but “cheap white labor did not emerge, and mountain inns and hotels faced a summer season without food, while lumber camps could not staff their cookhouses.”
Across California, near the start of the spring of 1886, “large-scale farmers, food processors, and cannery owners realized that they would not be able to carry on their businesses without the Chinese,” writes Pfaelzer.
Of course, all of these are just anecdotes about local effects. And, until recently, we’ve had no rigorous economic study of the effects of Chinese exclusion on the American economy. But in a new study, economists Nancy Qian, Joe Long, Carlo Medici, and Marco Tabellini provide just that.
The title of their working paper is “The Impact of the Chinese Exclusion Act on the economic development of the Western United States,” but Nancy Qian, an economist at Northwestern University, says their study’s estimated effects really include all the anti-Chinese laws, discrimination, and purges that affected Chinese Americans after 1882. “If vigilante violence and discrimination had been milder, then the anti-Chinese legislations would have probably had a smaller negative effect on the US economy,” Qian says. Namely, these laws would have reduced the inflow of Chinese immigrants, but they would not have caused as many Chinese Americans to flee communities, workplaces, and, more broadly, the United States.
In this way, Qian and her colleagues’ study may provide some insight into the effects not only of the restricted inflow of immigration — the official intent of the Chinese Exclusion Act — but also of mass deportations since many Chinese were forced out of communities and ultimately left the country.
Chinese immigrants had been vital to many West Coast industries. “By 1882, the Chinese had spread out across a lot of different sectors, and they were taking the skills that they had learned, mining, building the railroad, and also the ones they brought from China — they were applying it to lots of different things,” Qian says. This, she says, made the economy better for just about everyone.
“The sad punchline” of their study, Qian says, “is that very few people benefited from the Chinese Exclusion Act” and later laws and community actions. Western businesses suffered, and cities and towns across the West that saw their Chinese populations decline or disappear became less economically vibrant. For example, Qian and her colleagues find there was a slowdown in Western manufacturing, a sector in which many Chinese immigrants had worked.
The crackdown against Chinese immigrants, Qian says, hurt most of the white population in the West. And, further, it made West Coast towns and cities that had large Chinese populations in 1882 less of a magnet for white workers from the East because economic opportunities in these places shriveled. The economists find that Chinese exclusion, in its many 1882 and post-1882 incarnations, slowed down the economic growth and development of the West.
But Qian and her colleagues find there was at least one clear group of workers who benefited from Chinese exclusion: local white miners. It’s interesting because the first wave of Chinese immigrants who came here, after 1849, came to America with the hope of finding gold. And the first discriminatory laws they faced were at the local level and aimed to discourage Chinese immigrants from mining. It also provides more context for the resentment and rage of white miners that exploded in the Rock Springs massacre.
Mining is maybe more zero sum than other parts of the economy. There’s a fixed level of stuff in the ground and one person’s gain in finding valuable minerals is another person’s loss.
But Qian’s study suggests most of the economy didn’t work this way. It was not zero sum. Chinese workers actually improved the economic lives of most white workers and businessmen.
As a concrete example, she points to Chinese woodcutters. “So the Chinese workers — who were chopping down trees and making them into planks for the railroad — were now chopping down trees and making them into planks for the construction of houses and bars and hotels in western towns,” Qian says. “This is a very valuable skill. Now, all of a sudden, they leave. That doesn’t just affect the lumber mill. But you have to think about all the people who are relying on using the wood. So now the doctor’s office, the barmen, the hotel men, the railroad, everyone now has to pay more for wood. I mean, this is just a very important material for the whole economy.”
So, if there’s a lesson from Qian’s study, it’s that, yes, maybe immigration restrictions and expulsions or deportations can actually help some native workers. But, really, the cost is tremendous — not just for the immigrants themselves but also for almost everyone else.
The Recent Movement To Honor Chinese Victims
The story of what happened to Chinese immigrants is horrific. And in recent years, towns on the West Coast that purged their Chinese populations have begun to memorialize this dark period of history and honor the Chinese people who were kicked out of their towns.
For example, the city of Tacoma worked with the Chinese Reconciliation Project Foundation, a nonprofit, to create a park, which is called Tacoma Chinese Reconciliation Park.
Since 2021, an organization called the Eureka Chinatown Project has done various projects around Eureka to “honor the history and culture of the first Chinese people in Humboldt County, California” (the county Eureka is in).
Earlier this year, Truckee unveiled a plaque to commemorate the two Chinatowns that once existed in the town.
Many Americans remain ignorant of this history, and the organizers behind these projects want to educate them about it — with the hope history won’t repeat itself.
When researching this history, we read a number of illuminating books. We thank the historians for their work. You can check them out yourself:
Ghosts of Gold Mountain: The Epic Story of the Chinese Who Built the Transcontinental Railroad by Gordon H. Chang
Driven Out: The Forgotten War against Chinese Americans by Jean Pfaelzer
The Chinese Must Go: Violence, Exclusion, and the Making of the Alien in America by Beth Lew-Williams